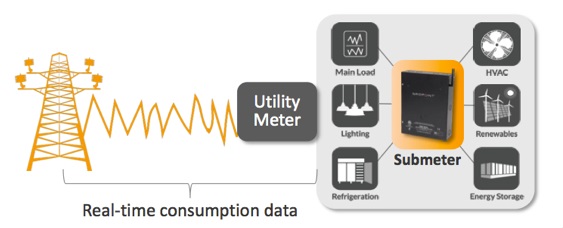
Sub Metering
Sub metering is an effective strategy for detailed energy management in buildings and facilities. It involves the installation of additional meters to monitor energy consumption at a more granular level, such as individual tenants, departments, equipment, or specific areas within a building.
Key Components and Types of Sub Metering:
-
Electric Sub Meters:
- Measure electricity usage at specific circuits or equipment levels.
- Common in commercial buildings, industrial facilities, and multi-tenant buildings.
-
Water Sub Meters:
- Monitor water usage in different areas or by specific tenants.
- Essential for identifying leaks and promoting water conservation.
-
Gas Sub Meters:
- Track natural gas consumption for heating, cooking, or industrial processes.
- Useful for managing energy costs in facilities with significant gas usage.
-
Thermal Sub Meters:
- Measure the consumption of heating and cooling energy (e.g., steam, hot water, chilled water).
- Common in buildings with central HVAC systems
Benefits of Sub Metering:
-
Detailed Energy Monitoring:
- Provides precise data on energy consumption for specific areas, tenants, or equipment.
- Helps identify inefficiencies and areas for improvement.
-
Cost Allocation:
- Enables accurate billing for energy usage in multi-tenant buildings or shared spaces.
- Encourages tenants to be more energy-conscious and responsible.
-
Energy Savings:
- Pinpoints high-energy-use areas or equipment, allowing for targeted energy-saving measures.
- Supports the implementation of energy efficiency projects and tracking of their impact.
-
Enhanced Control:
- Provides building managers with the information needed to optimize energy use.
- Facilitates the proactive management of energy consumption, reducing waste.
-
Regulatory Compliance:
- Helps buildings meet regulatory requirements and energy efficiency standards.
- Supports reporting for energy certification programs (e.g., LEED, ENERGY STAR).